Quick Reference Card
2 Pages
Preview
Page 1
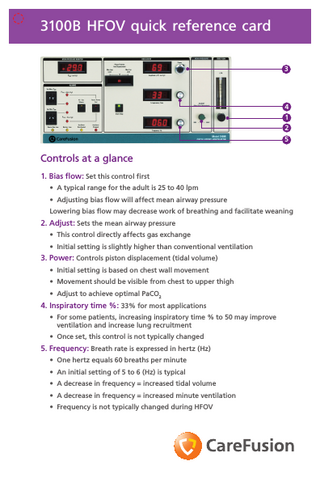
3100B HFOV quick reference card 3
4 1 2 5
Controls at a glance 1. Bias flow: Set this control first • A typical range for the adult is 25 to 40 lpm • Adjusting bias flow will affect mean airway pressure Lowering bias flow may decrease work of breathing and facilitate weaning
2. Adjust: Sets the mean airway pressure • This control directly affects gas exchange • Initial setting is slightly higher than conventional ventilation
3. Power: Controls piston displacement (tidal volume) • Initial setting is based on chest wall movement • Movement should be visible from chest to upper thigh • Adjust to achieve optimal PaCO2
4. Inspiratory time %: 33% for most applications • For some patients, increasing inspiratory time % to 50 may improve ventilation and increase lung recruitment • Once set, this control is not typically changed
5. Frequency: Breath rate is expressed in hertz (Hz) • One hertz equals 60 breaths per minute • An initial setting of 5 to 6 (Hz) is typical • A decrease in frequency = increased tidal volume • A decrease in frequency = increased minute ventilation • Frequency is not typically changed during HFOV
Weaning guidelines While on HFOV: • Wean FiO2 as tolerated to target FiO2 • Once FiO2 is < target FiO2 , begin to wean mean airway pressure by increments of 1 to 2 cmH2O • Assess for adequate lung inflation and PaO2
In air leak syndrome: Mean airway pressures are similar to those used in conventional ventilation; higher FiO2s are typically used
Transition to conventional ventilation when each of the following parameters are met:
1. Mean airway pressure is stable and appropriate for the pathology 2. Patient tolerates position changes and procedures well 3. Gas exchange and lung volumes are acceptable and stable When returning a patient to conventional ventilation, mean airway pressure values should remain similar to those employed in HFOV. Weaning from conventional ventilation should follow individual institutional practice. These are general guidelines only and assume the clinician has read and understands the 3100B operator’s manual. The physician must determine the appropriateness of these guidelines as they apply to specific patients.
Valve assembly locations Red: Dump valve, mid expiratory limb Green: Mean airway pressure, expiratory limb Blue: Limit valve, inspiratory limb
Figure 1
Mean airway pressure Mean airway pressure is regulated by controlling the inflation of the balloon valve in the expiratory limb of the circuit (Figure 1). As inflation pressure inside the balloon increases, the outflow of gas is restricted, providing mean airway pressure. CareFusion 22745 Savi Ranch Parkway Yorba Linda, CA 92887 800.231.2466 toll-free 714.283.2228 tel 714.283.8493 fax
CareFusion Germany 234 GmbH Leibnizstrasse 7 97204 Hoechberg Germany +49 931 4972-0 tel +49 931 4972-423 fax
CareFusion Yorba Linda, CA
carefusion.com © 2010 CareFusion Corporation or one of its subsidiaries. All rights reserved. RC1806 (1110/1000) L2323 Rev. B