Quick Reference Card
2 Pages
Preview
Page 1
3100A Quick Reference Card 3
4 5
1 2
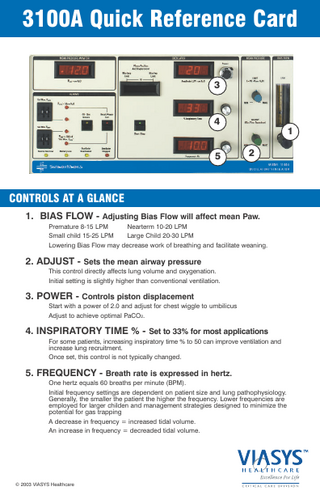
CONTROLS AT A GLANCE 1. BIAS FLOW - Adjusting Bias Flow will affect mean Paw. Premature 8-15 LPM Nearterm 10-20 LPM Small child 15-25 LPM Large Child 20-30 LPM Lowering Bias Flow may decrease work of breathing and facilitate weaning.
2. ADJUST - Sets the mean airway pressure This control directly affects lung volume and oxygenation. Initial setting is slightly higher than conventional ventilation.
3. POWER - Controls piston displacement Start with a power of 2.0 and adjust for chest wiggle to umbilicus Adjust to achieve optimal PaCO2.
4. INSPIRATORY TIME % - Set to 33% for most applications For some patients, increasing inspiratory time % to 50 can improve ventilation and increase lung recruitment. Once set, this control is not typically changed.
5. FREQUENCY - Breath rate is expressed in hertz. One hertz equals 60 breaths per minute (BPM). Initial frequency settings are dependent on patient size and lung pathophysiology. Generally, the smaller the patient the higher the frequency. Lower frequencies are employed for larger childen and management strategies designed to minimize the potential for gas trapping A decrease in frequency = increased tidal volume. An increase in frequency = decreaded tidal volume.
© 2003 VIASYS Healthcare
WEANING GUIDELINES WHILE ON HFOV: Wean FiO2 as tolerated to target FiO2. Once FiO2 is < target FiO2, begin to wean mean airway pressure by increments of 1-2 cmH2O. Assess for adequate lung inflation with chest x-ray and arterial PO2. Assess oxygenation with pulse oximetry.
IN AIR LEAK SYNDROME: Mean airway pressures are similar to those used in conventional ventilation. Higher FiO2's are typically used.
TRANSITION TO CONVENTIONAL VENTILATION, NCPAP, or Nasal Cannula, when each of the following parameters are met: 1) Mean airway pressure is stable and appropriate for the pathology 2) Patient tolerates position changes and procedures well 3) ABG's are acceptable and stable These guidelines are recommedations only. For any treatment each physician must determine the appropriateness of these guidelines as they apply to specific patients.
VALVE ASSEMBLY LOCATIONS A. Red - Dump Valve, mid expiratory limb. B. Green - Mean Airway Pressure, expiratory limb. C. Blue - Limit Valve, inspiratory limb
A
B C
FIGURE 1
MEAN AIRWAY PRESSURE Mean airway pressure is regulated by controlling the inflation of the balloon valve in the expiratory limb of the circuit (Figure 1). As inflation pressure inside the balloon increases, the outflow of gas is restricted, providing mean airway pressure.
VIASYS Healthcare - Critical Care Division 22705 Savi Ranch Parkway Yorba Linda, CA 92887 714-283-1830 • 800-520-4368 Fax 714-283-8493 P/N 775895-101A
www.ViasysCriticalCare.com
VIASYS Healthcare Rembrandtlaan 1b 3723 BG Bilthoven The Netherlands (31) 30 2289711 Fax (31) 30 2286244